
List of all publications from the Ellmeier Lab – click here 
Manuscripts uploaded on bioRxiv (not peer-reviewed preprints) – click here 
Publication highlights
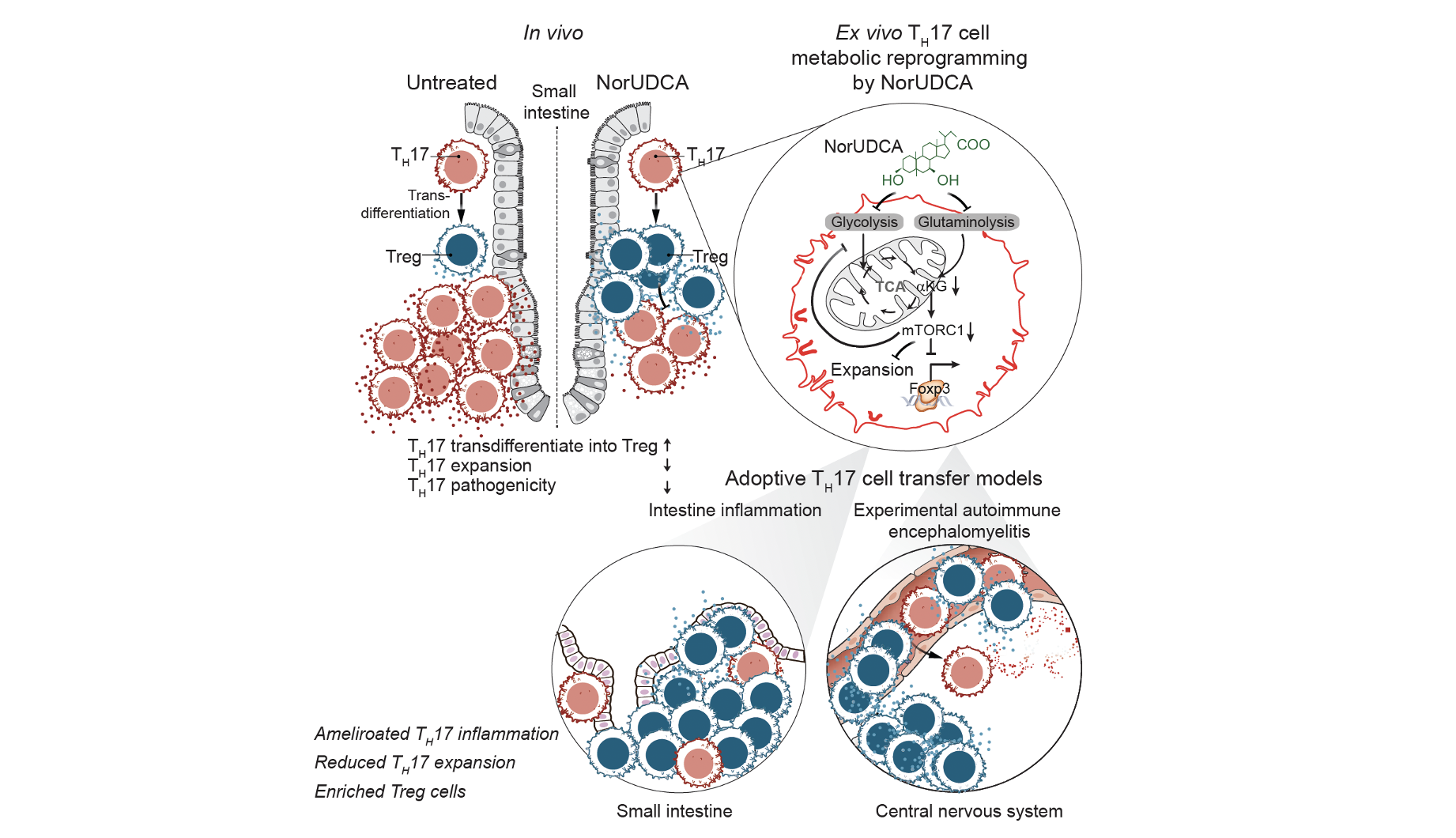
24-Nor-ursodeoxycholic acid improves intestinal inflammation by targeting TH17 pathogenicity and transdifferentiation
Zhu C, et al, … Ellmeier W* and Trauner M* (2025). Gut, gutjnl-2024-333297
PubMed link
more information …
24-Nor-ursodeoxycholic acid (NorUDCA) is a novel therapeutic bile acid for treating immune-mediated cholestatic liver diseases, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). Since PSC strongly associates with T helper-type-like 17 (TH17)-mediated intestinal inflammation, we explored NorUDCA’s immunomodulatory potential on TH 17 cells. In this study we uncover that NorUDCA restricts TH17 inflammation in multiple mouse models including humanised NSG mice reconstituted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with PSC. Our study potentiates future clinical applications of NorUDCA for treating TH 17-mediated intestinal diseases and beyond.
*shared corresponding authors
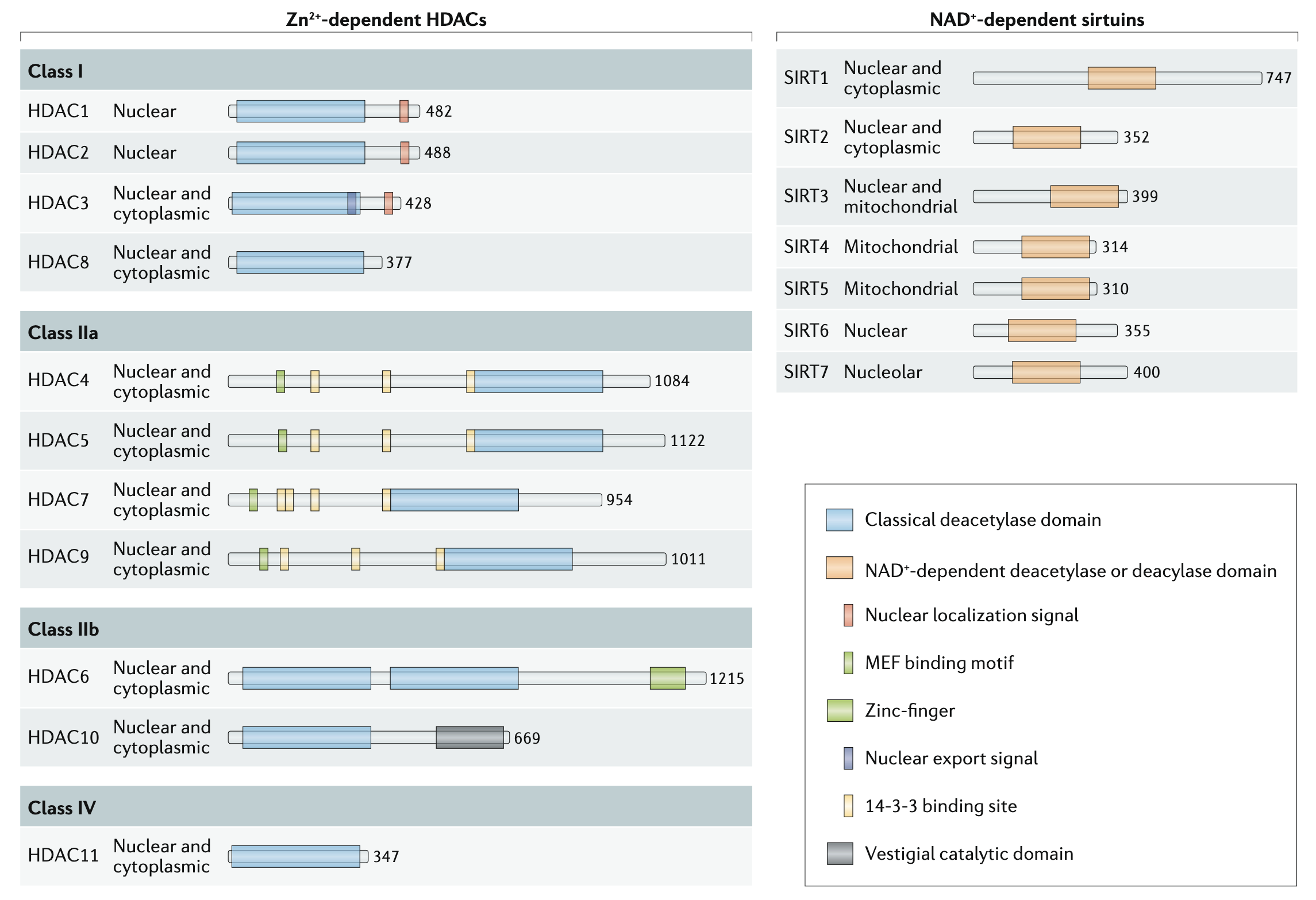
Histone deacetylase function in CD4+ T cells
Ellmeier W and Seiser C. (2018). Nature Reviews Immunology, 18, 617-634.
PubMed link
more information …
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone acetyltransferases mediate reversible acetylation of histones and many other non-histone proteins to regulate gene expression and protein function. Here, we describe the myriad activities of HDACs in CD4+ T cells and the potential use of HDAC inhibitors as therapeutics for immune-mediated diseases.
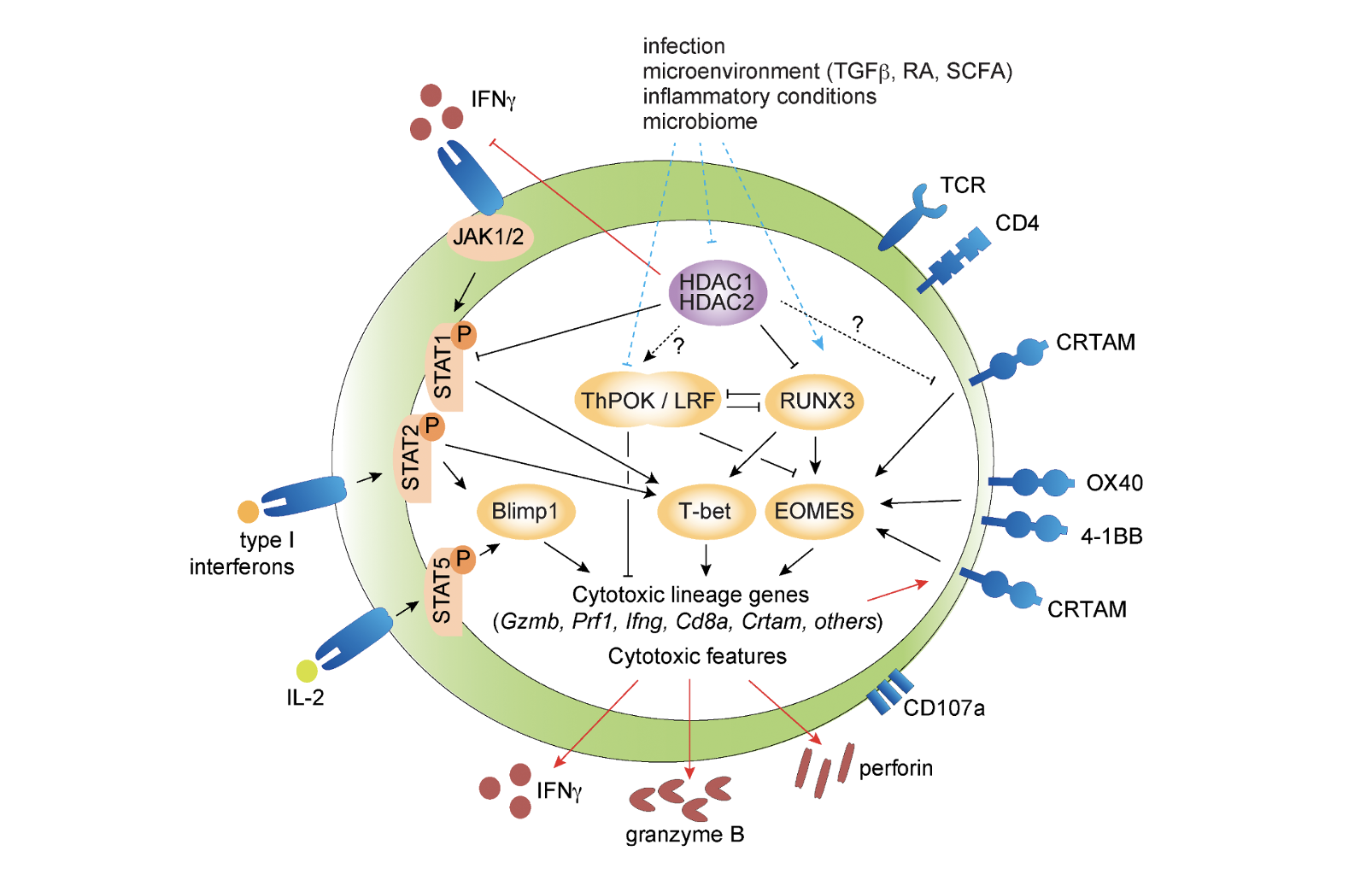
CD4+ Cytotoxic T cells – Phenotype, Function and Transcriptional Networks Controlling Their Differentiation Pathways
Preglej T and Ellmeier W. (2022). Immunology Letters, 247:27-42.
PubMed link
more information …
In this review, we provide a brief overview about key features of CD4 CTLs, including their role in viral infections and cancer immunity, and about the link between CD4 CTLs and immune-mediated diseases. Subsequently, we will discuss the current knowledge about transcriptional and epigenetic networks controlling CD4 CTL differentiation and highlight recent data suggesting a role for histone deacetylases in the generation of CD4 CTLs.
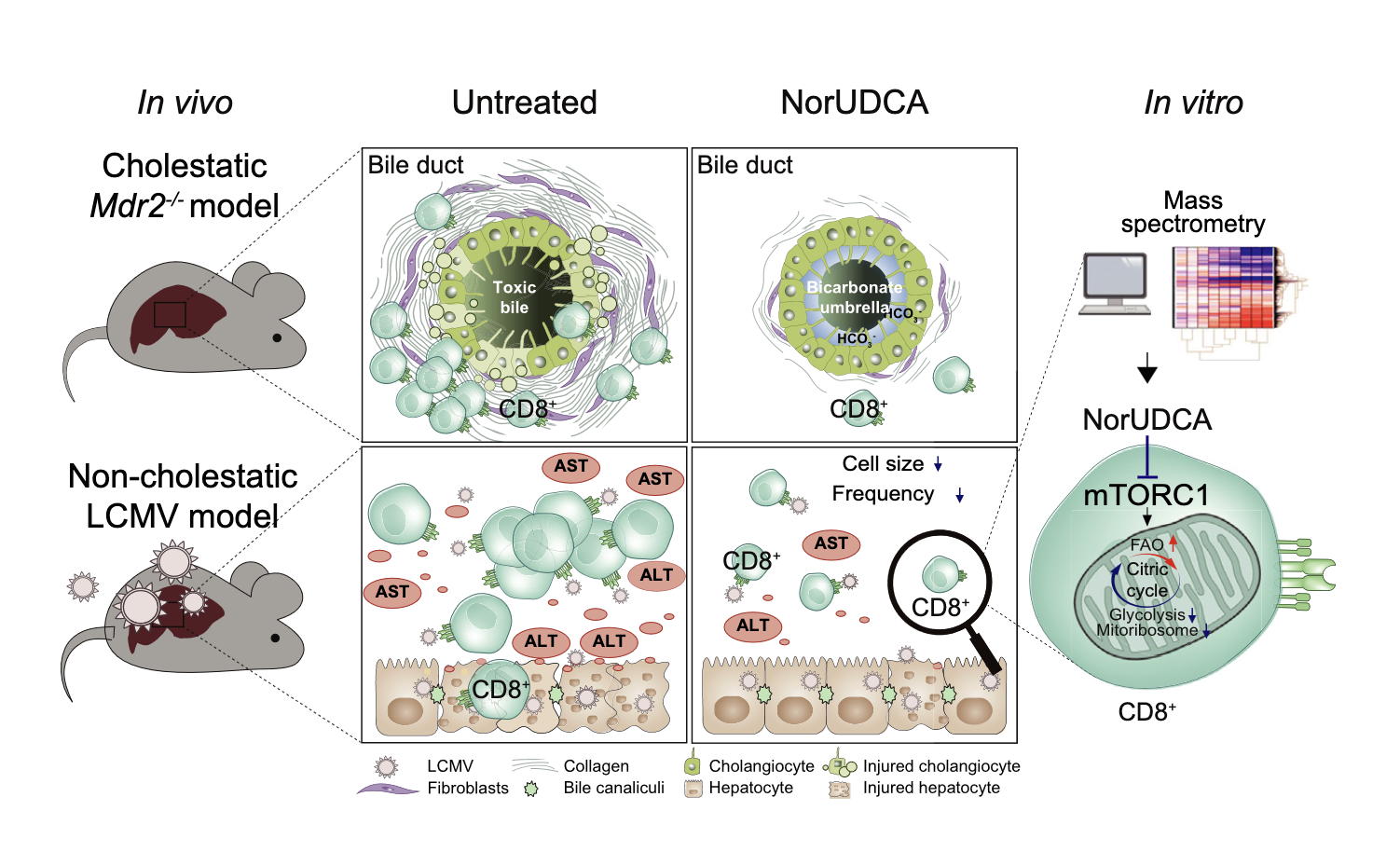
24-Norursodeoxycholic acid reshapes immunometabolism in CD8+ T cells and alleviates hepatic inflammation
Zhu C, Boucheron, N et al … and Ellmeier W, Trauner M. (2021). Journal of Hepatology, 75(5):1164-1176.
PubMed link
more information …
24-Norursodeoxycholic acid (NorUDCA) is a novel therapeutic bile acid used to treat immune-mediated cholestatic liver diseases, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), where dysregulated T cells including CD8+ T cells contribute to hepatobiliary immunopathology. In this study, we uncovered that NorUDCA has a direct modulatory impact on CD8+ T cells and attenuates excessive CD8+ T cell-driven hepatic immunopathology. These findings are relevant for treatment of immune-mediated liver diseases such as PSC.
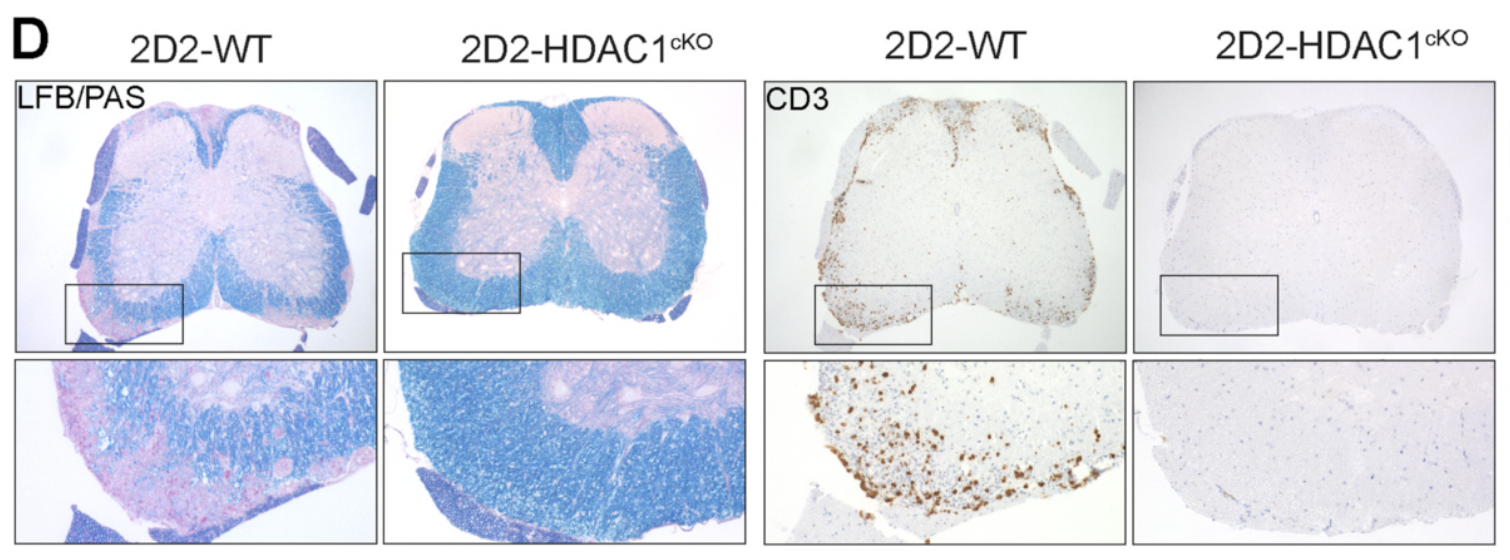
Histone deacetylase 1 controls CD4+ T cell trafficking in autoinflammatory diseases
Hamminger P, et al … and Ellmeier W. (2021). Journal of Autoimmunity, 119:102610.
PubMed link
more information …
CD4+ T cell trafficking is a fundamental property of adaptive immunity. In this study, we uncover a novel role for HDAC1 in controlling effector CD4+ T cell migration, thereby providing mechanistic insight into why a T cell-specific deletion of HDAC1 protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE).
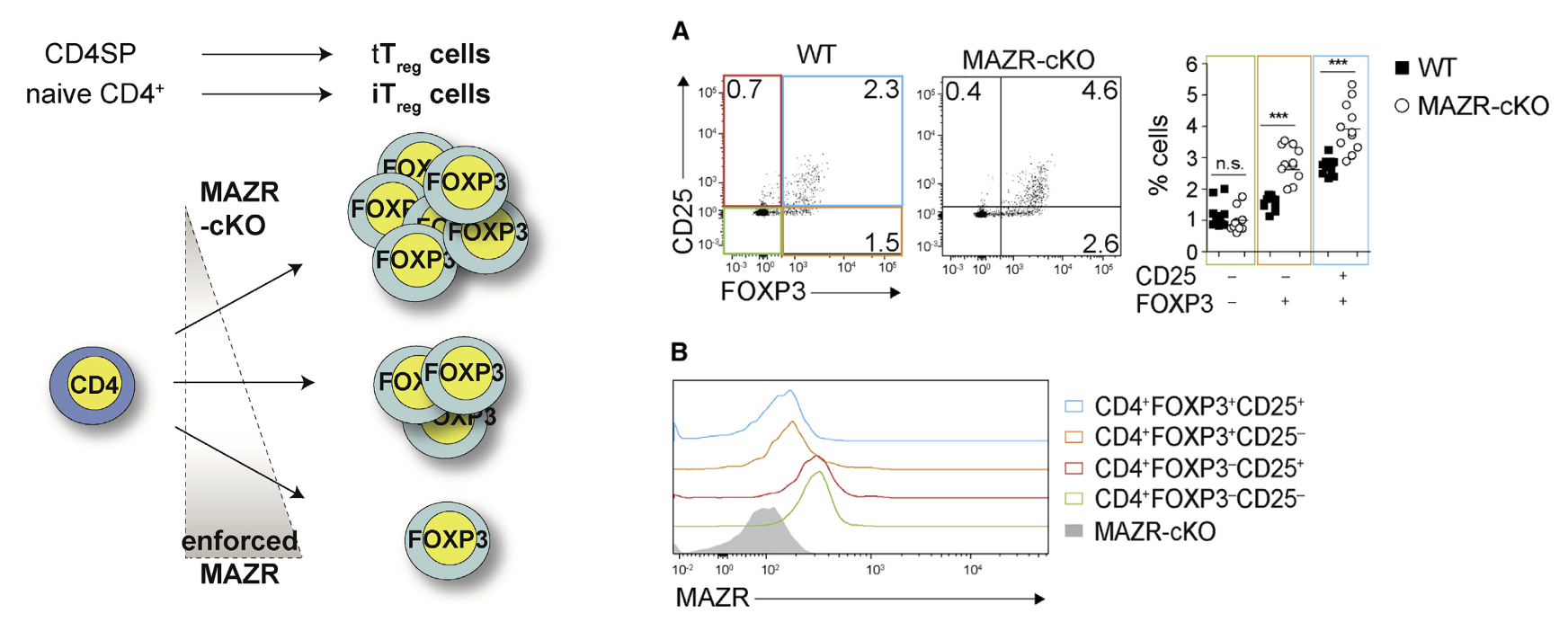
The Transcription Factor MAZR/PATZ1 Regulates the Development of FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells
Andersen L et al … and Ellmeier W. (2019). Cell Reports, 29(13):4447-4459.e6.
PubMed link
more information …
FOXP3+ Treg cells are essential for maintaining tolerance and immune homeostasis. Here we reveal that MAZR is an important factor in regulating the delicate balance of Treg cell generation and report that MAZR expression levels play a key role in controlling Treg cell development and differentiation.
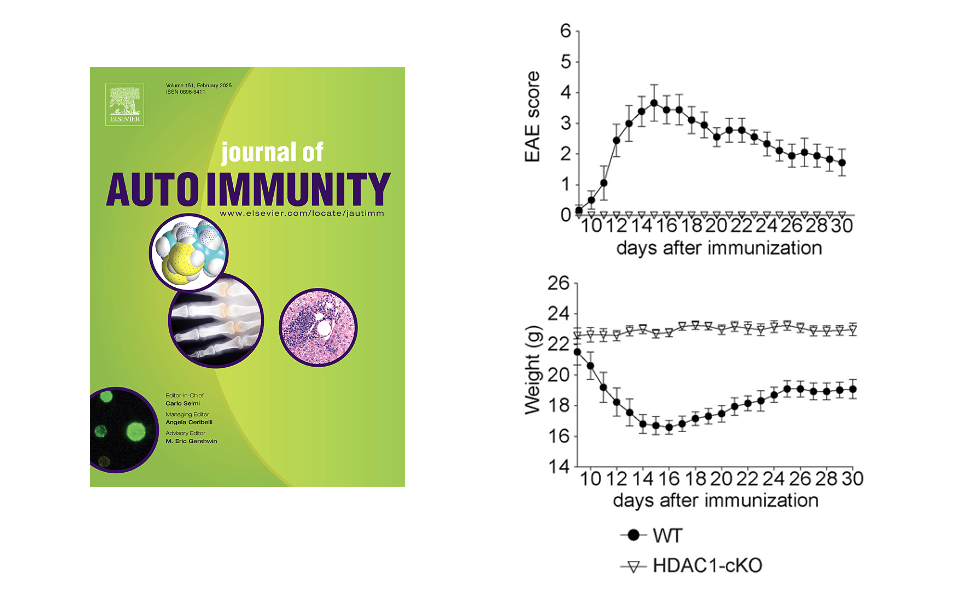
A T cell-specific deletion of HDAC1 protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Göschl L, et al … and Ellmeier W. (2017). Journal of Autoimmunity, 86:51-61.
PubMed link
more information …
Here were report that HDAC1 function in T cells is important for the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. These data suggest that selective inhibition of HDAC1 might be a novel treatment strategy for multiple sclerosis.
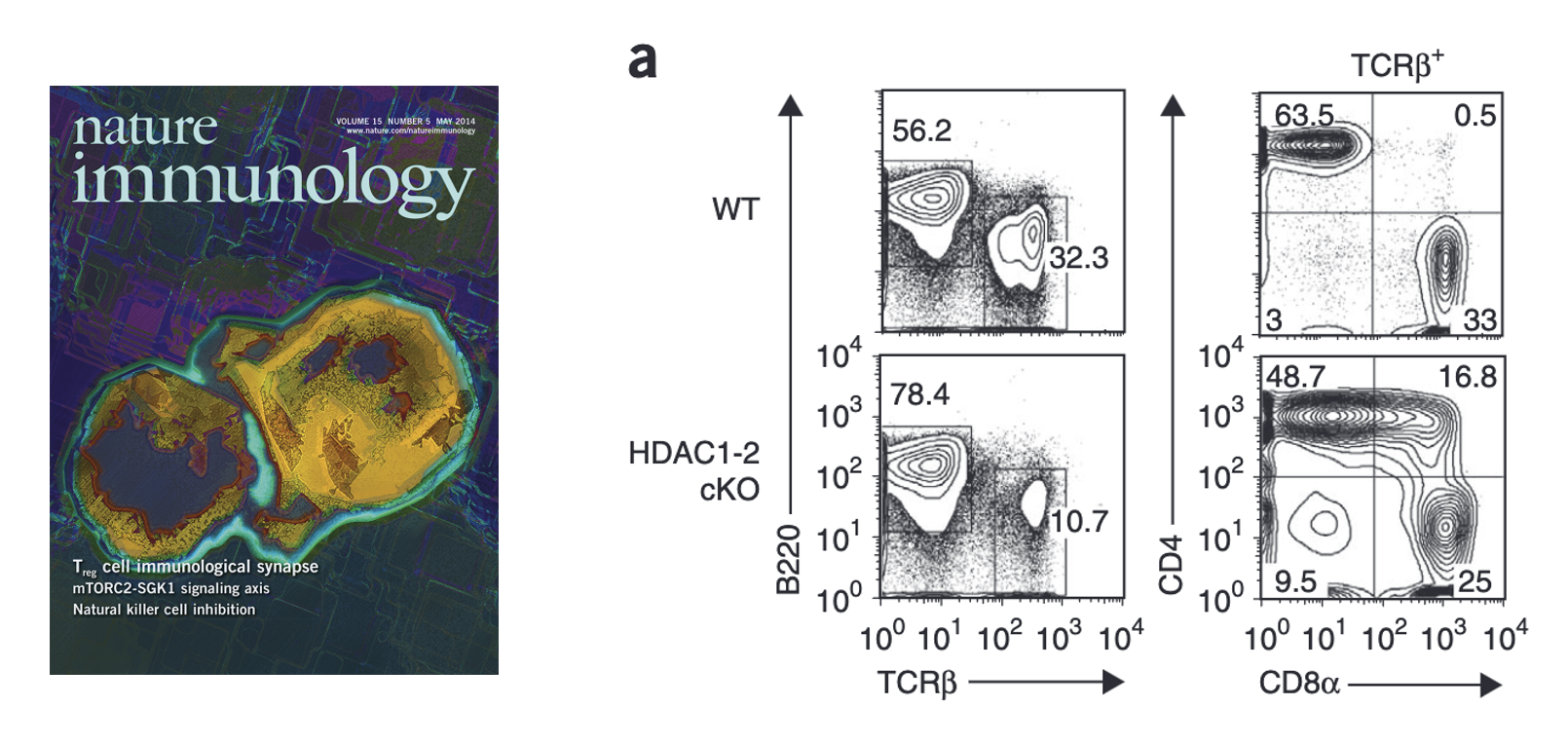
CD4 T cell lineage integrity is controlled by the histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2
Boucheron, N, Tschismarov, R, et al … and Ellmeier, W.* (2014). Nature Immunology, 15(5):439-48.
PubMed link
more information …
Here we revealed an unexpected plasticity of CD4+ T cells towards the cytotoxic lineage. We demonstrate that HDAC1 and HDAC2 are essential to maintain the integrity of CD4+ T cells by repressing repressing Runx-CBFβ complexes that otherwise induce a CD8+ effector T cell-like program in CD4+ T cells.
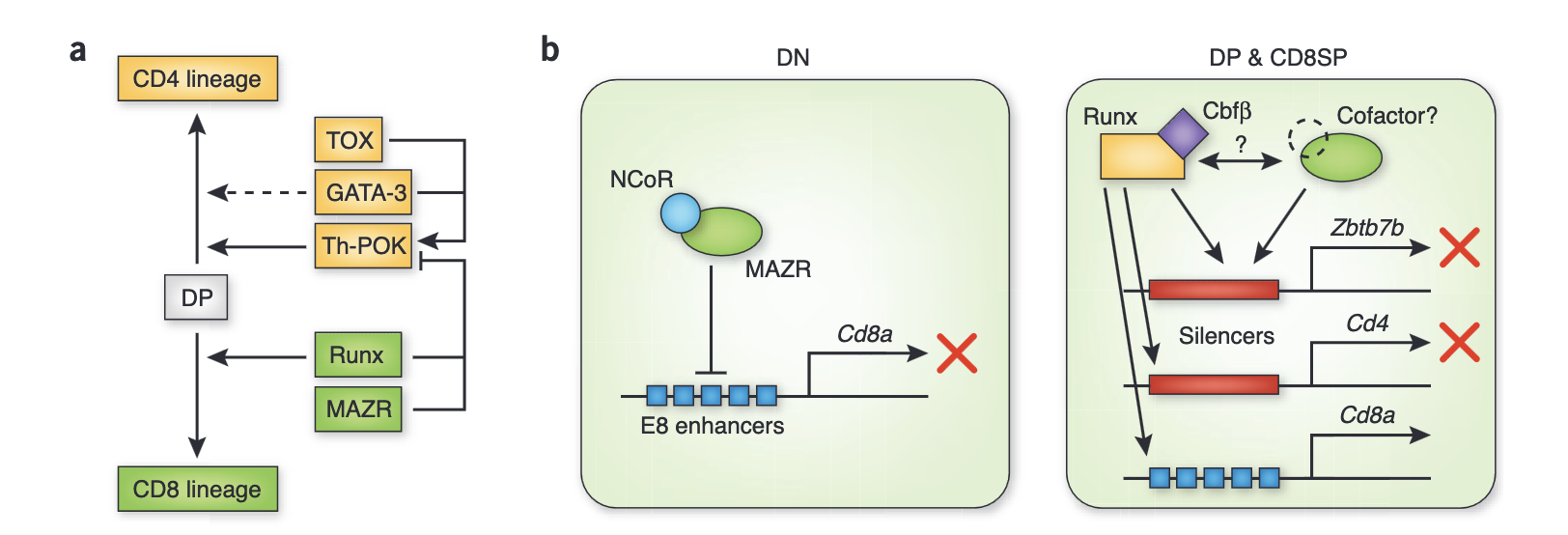
The zinc-finger protein MAZR is part of the transcription factor network that controls the CD4 versus CD8 lineage fate of double-positive thymocytes
Sakaguchi S, et al … and Ellmeier, W. (2010). Nature Immunology, 11:442-8 (selected in News & Views section – Nat Immunol 11, pages 370–371 (2010); see picuture below). PubMed link
more information …
Here we identified that MAZR regulates CD8 lineage differentiation by repressing ThPOK in MHC class I-signaled DP thymocytes.